Batches
Data annotation is an integral part of the AI solution development pipeline, regardless of its size and complexity. AI teams use annotation tools to get through this stage. Unfortunately, as the projects' size scales, teams struggle to process a significant amount of raw data that should be annotated and reviewed because of multiple disjointed collaborators involved.
To address this challenge and support you across the workflow, CloudFactory's annotation tool has several built-in features that aim to help developers organize and track the annotation workstream and collaborate with others in real time.
Utilizing these features in the workstream allows all the users to:
- Communicate with each other in real-time;
- Organize and operate with data in batches;
- Add specific labeling instructions for the annotation work;
- Automatically distribute and assign specific data for annotation to a specific expert annotator.
Let's touch on the Batches feature.
Batches explained
CloudFactory's Batches feature allows users to organize stored data into different entities, adding a layer of flexibility to projects.
With Batches, it is possible to add data into a batch and easily track its progress on annotation and QA processes, all the way to completed structured data ready for export or reporting. Understanding the progress of the data can help AI teams manage large annotation projects with many contributors doing different tasks simultaneously. Also, with the Batches feature, organizing specific or special data, such as edge cases or data that needs special care or attention, is a piece of cake.
Creating and Managing Batches
The Batches page is in the 'File Manager' in the project navigation. By default, there are no pre-built Batches in the project. You can create a Batch by clicking on the 'Create batch' button; a modal will open where you can add your Batch title based on your project’s needs. Once the Batch is created, a batch card will be displayed on the page. You can create an unlimited number of Batches to organize your project.
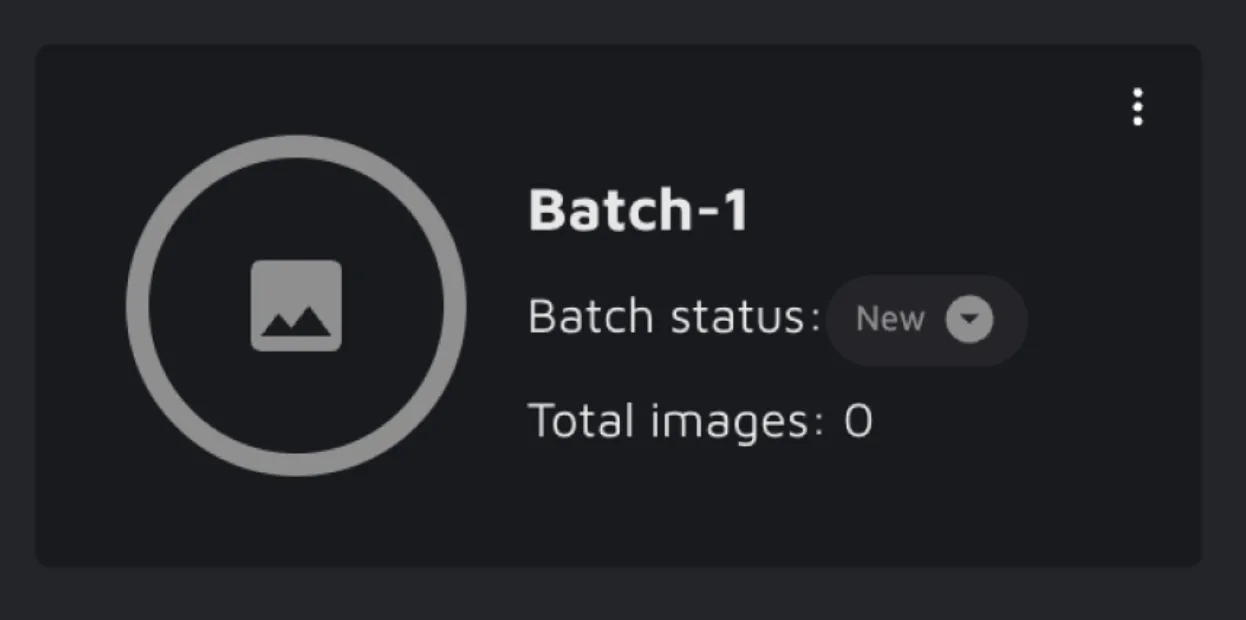
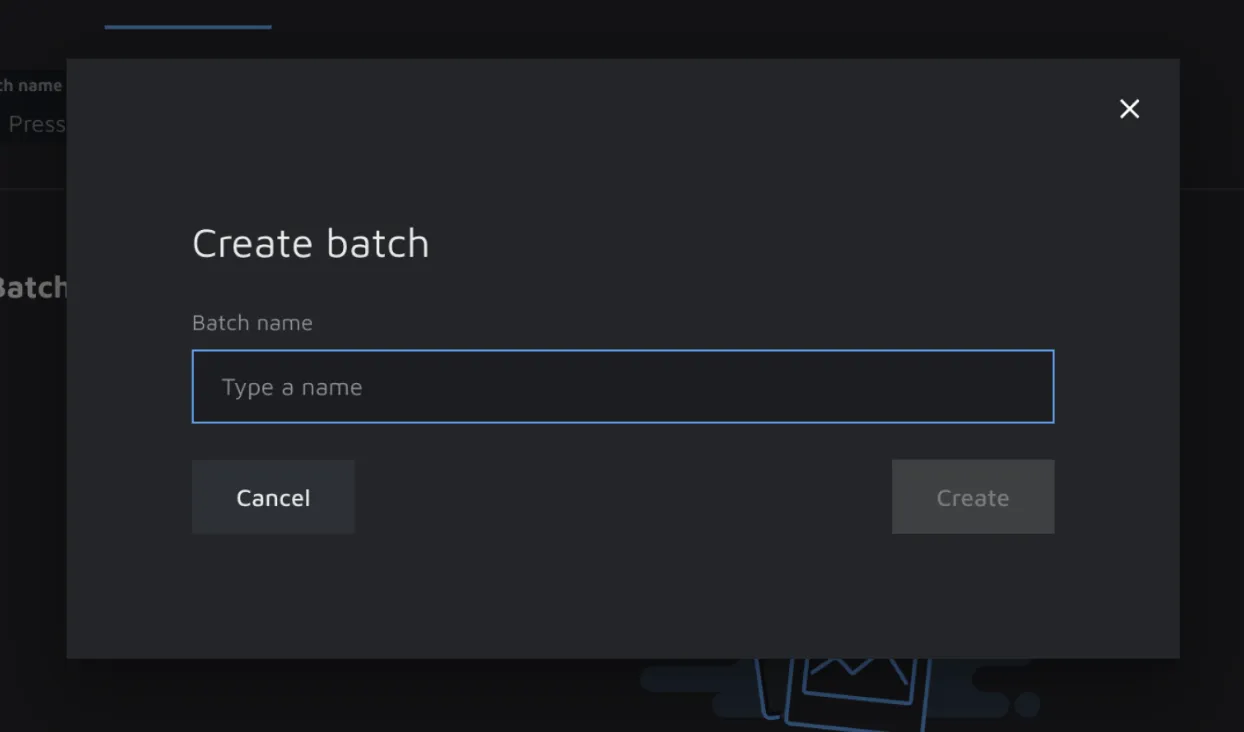
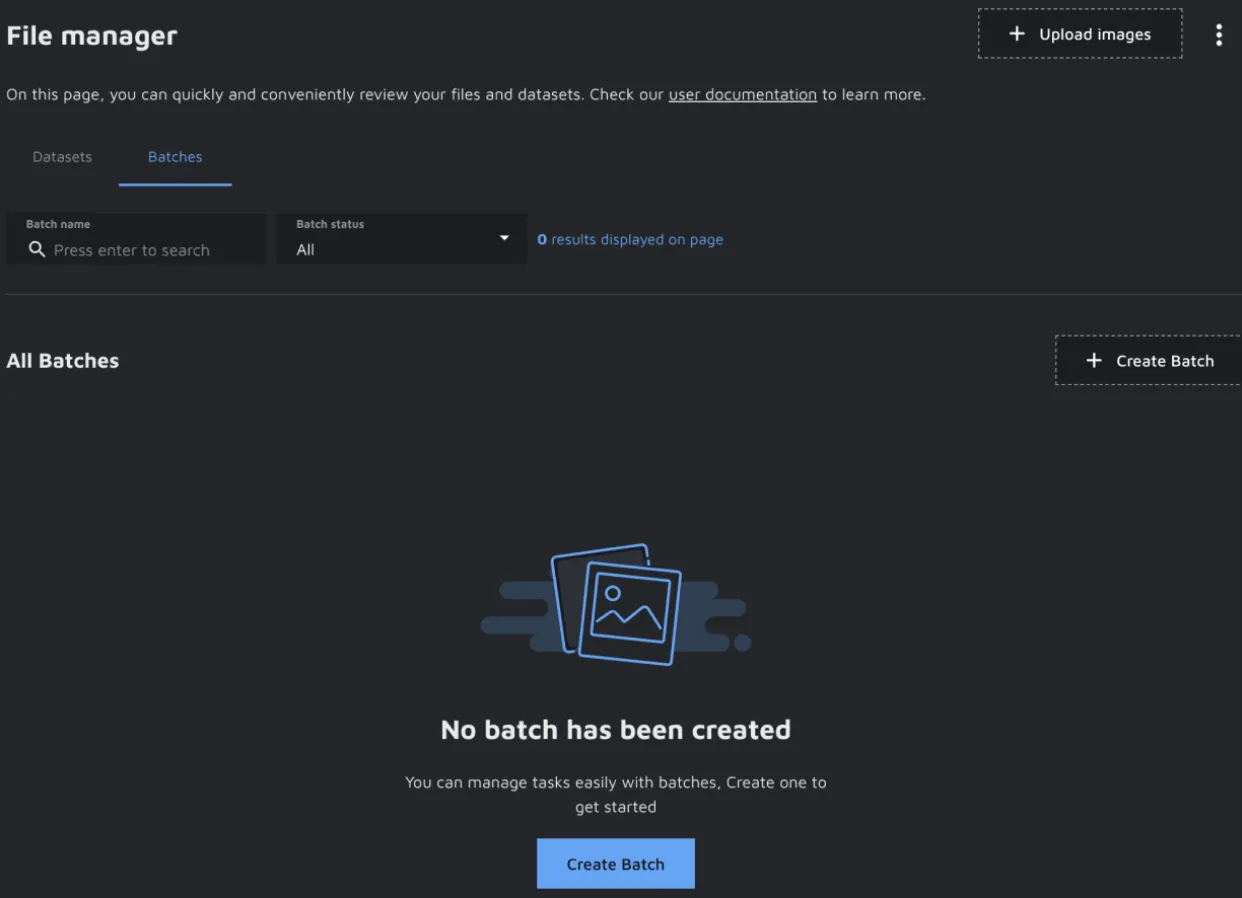
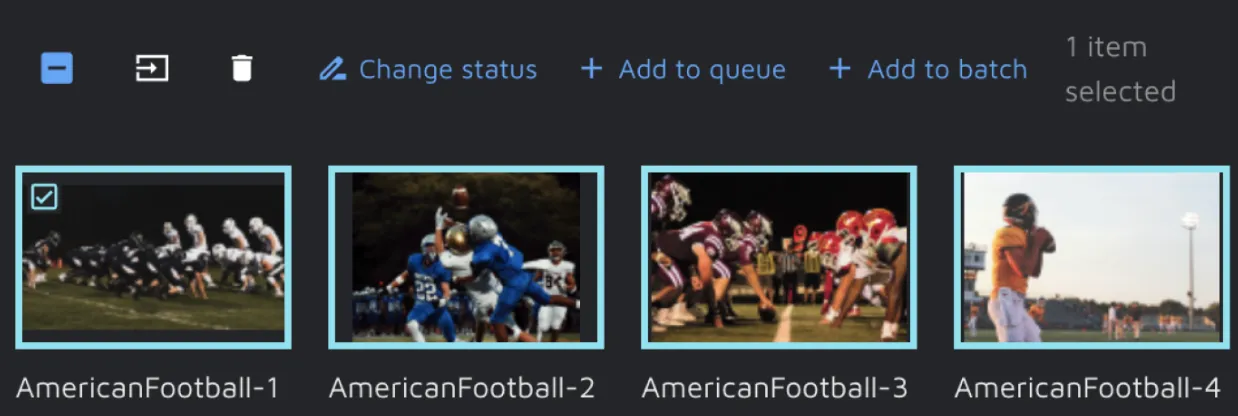
The Batch you just created will be empty at first, with the status 'New'. To get started, you will need to add some data to your Batch. You can select files in the 'File Manager' and add them to a Batch. In the modal, you can specify which one they should go in.
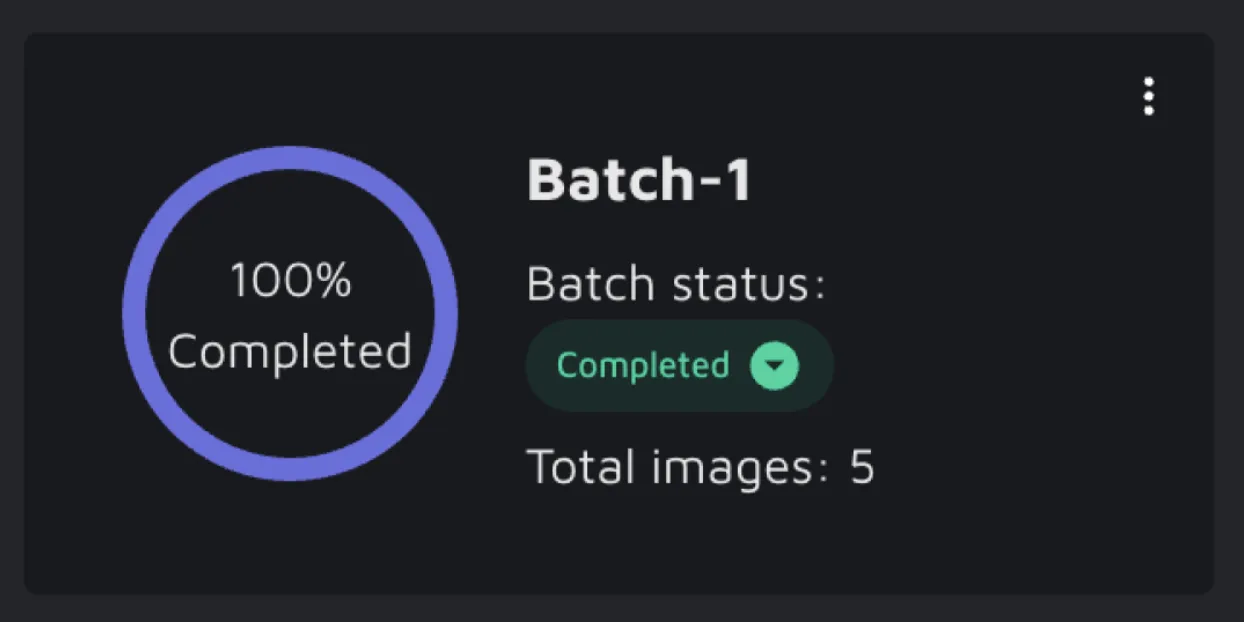
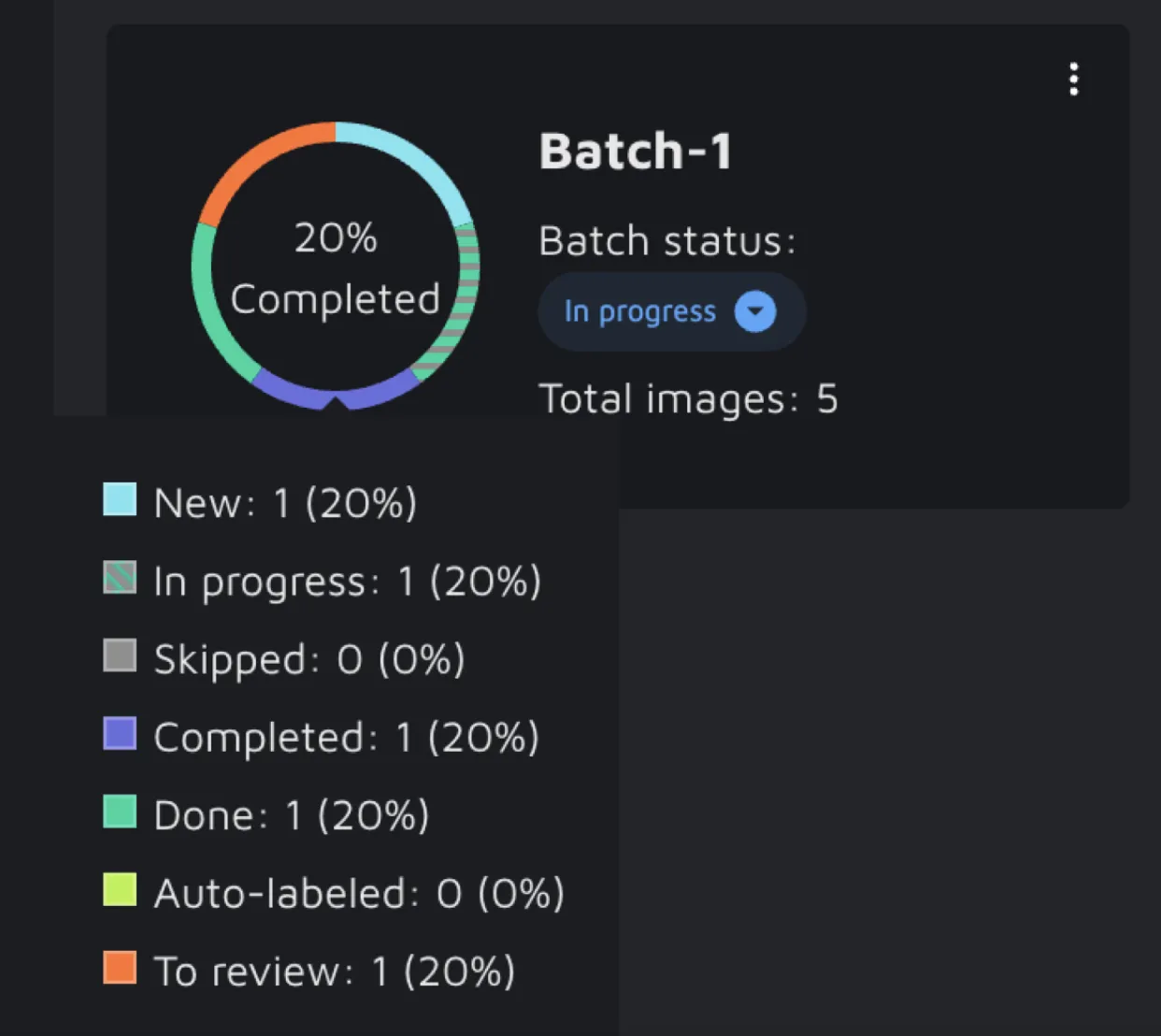
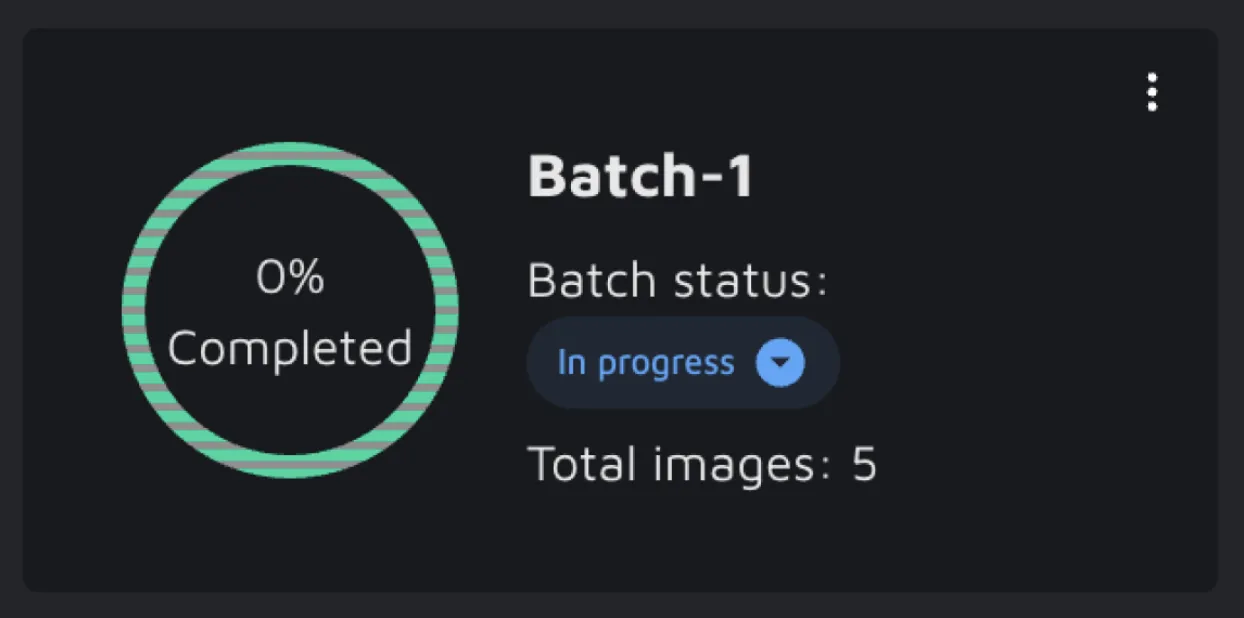
On the Batch overview page, you can see the work progress in your Batches based on data status. Your files' assigned status reflects the Batch's progress, which is displayed in percentages. On hovering over the Batch card, you get to see a detailed breakdown of numbers and percentages. Another way to keep track of all your batches is to change their status manually. By default, a Batch is New, and you can change that to 'In progress' and 'Completed'. This can help you quickly grasp the that work was completed or the one that still needs to get done.
Batch functionality
The Batch has some interesting features that might help you manage your data. Clicking on the options menu on the Batch card shows you those functionalities: 'Manage files', 'Add to Queue', and 'Empty/Remove batch'.
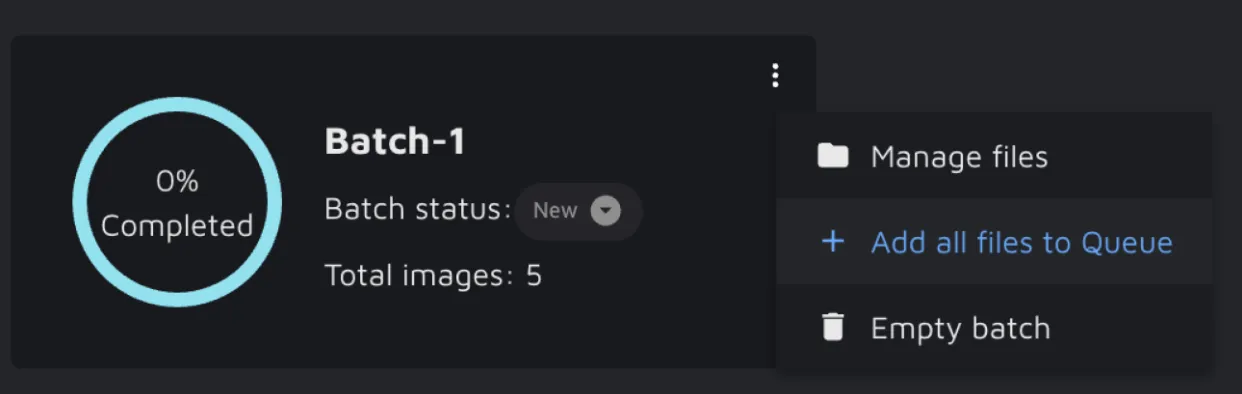
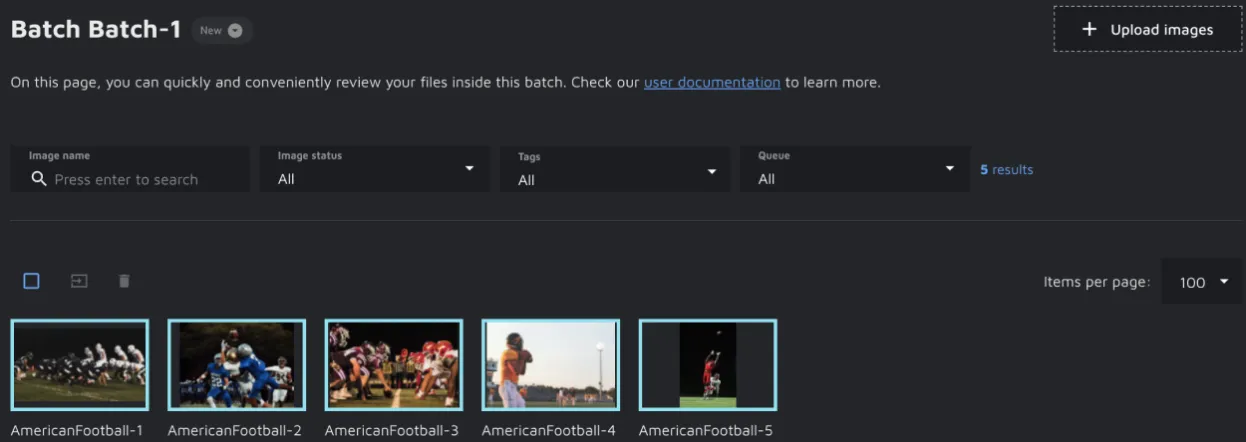
'Manage files' will open a detailed view of the images in your Batch. Here you can filter and select all the images and change their status, remove them from a batch or add them to a queue.
'Add to Queue' will add all the images in the Batch to a Queue of your choice, turning them into tasks to be picked up by others.
You can only remove a batch once it is empty. When there is any data in the Batch, you can click 'Empty batch' and safely remove it. Removing a file from a batch does not mean that it is removed from your project. The file will still be available in their original dataset, which you can find in the 'File Manager'.
