Queues
Data annotation is an integral part of the AI solution development pipeline, regardless of its size and complexity. AI teams use annotation tools to get through this stage. Unfortunately, as the projects' size scales, teams struggle to process a significant amount of raw data that should be annotated and reviewed because of multiple disjointed collaborators involved.
To address this challenge and support you across the workflow, CloudFactory's annotation tool has several built-in features that aim to help developers organize and track the annotation workstream and collaborate with others in real time.
Utilizing these features in the workstream allows all the users to:
- Communicate with each other in real-time;
- Organize and operate with data in batches;
- Add specific labeling instructions for the annotation work;
- Automatically distribute and assign specific data for annotation to a specific expert annotator.
Let's touch on the Queues feature.
Queues explained
CloudFactory's Queue feature turns your data into tasks. Specific users (users with specific permissions) can add data to the queue; others can receive this data as labeling tasks to pick up and complete. When using Queues to distribute tasks, you can set certain settings to ensure the efficiency of the annotation process. This way, it is possible to eliminate manual processes in task distribution and add an additional level of control over the data annotation process.
Activating and Setting up Queues
To activate Queues, please navigate to the 'Project Setup => Tool preferences' page. On this page, you can select all the features and tools you want to activate or disable for your project. Once you toggle the Queues flag there, please navigate back to the Project Dashboard for the next steps.
When Queues are active, you will see two Queue cards on your dashboard: the Labeling queue and Review queue. You can use those two queues for annotation and QA cycles. By default, both Queues are disabled to allow you to adjust your settings and add data.
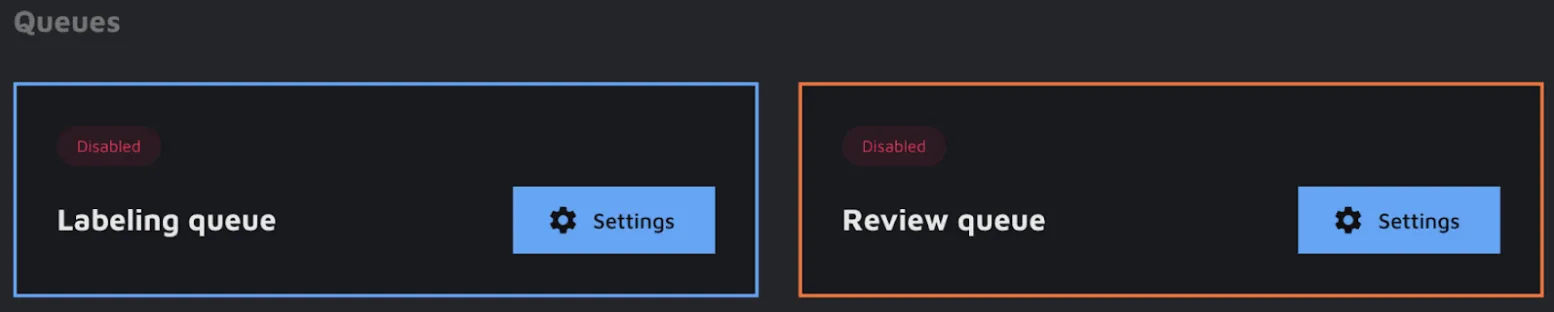
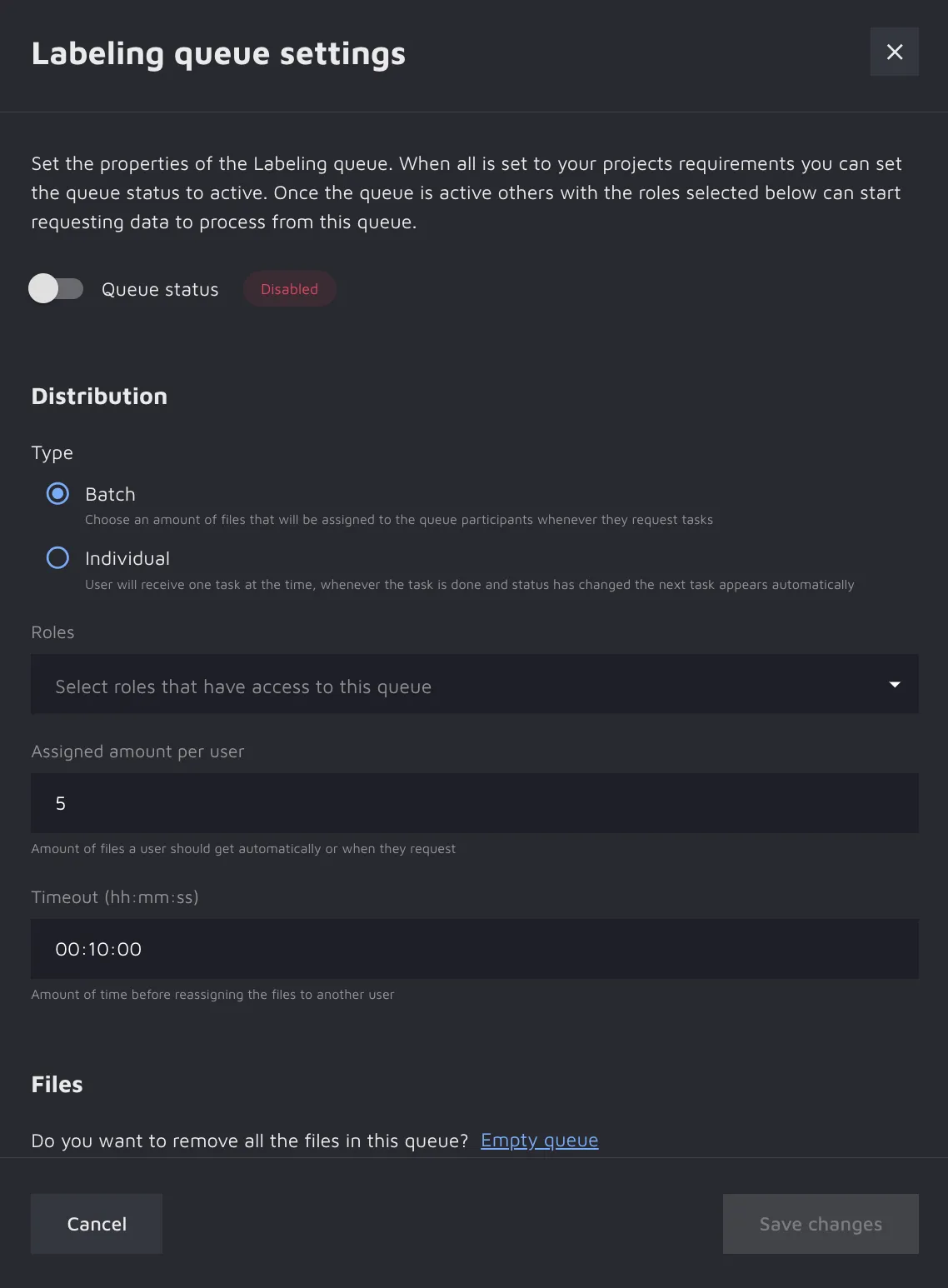
Clicking on the 'Settings' button on either of your Queue cards will open a side modal with all the available options. Let’s go through them to help you set it up.
- Status: This shows whether the queue is active or not active. When a queue is active, a user attached to the queue by role (see role explanation below) can fetch tasks from that queue. Controlling the status setting can be helpful to make sure the right data is in the queue before it becomes active;
- Type: This defines the distribution type you want Queue to perform. You can choose a batch and set the amount of data (see Assigned amount per user below) if you’d like people to fetch tasks in a batch, for example, where context or copying labels is relevant. The other option would be to send out tasks one by one, only sending one when the previous task is completed;
- Role: This defines who can fetch tasks from the Queue you are setting up. You can choose any role available in the project besides the Owner. For example, you can add 10 users to your project and assign them the Labeler role. Those 10 users are now able to fetch data from the Queue once it is active and data is available;
- Assigned amount per user: This defines how much data the user will receive at once upon the request. If you have chosen to distribute the data individually, this field will be frozen;
- Timeout time: This defines how long a batch of tasks stays with one specific user after requesting them. After the time runs out, any tasks that are left are put back at the top of the queue and distributed to a different user upon request;
- Empty Queue: This option allows you to simultaneously remove all the data from the queue.
Adding data to the Queue
Now that the Queues have all the settings you and your workflow require, you can add your data. You can add data to a Queue from the 'File Manager', located in the project navigation.
Upon selecting an image or multiple images, the button 'Add to Queue' appears. On clicking, you will see a modal that asks you to define which queue this image or set of images should go. After selecting, a tag will appear on the images present at that time in the Queue so you can keep track. You can repeat this logic for single images, multiple images, a dataset, and even for AI Consensus Scoring results.
If you would like to prioritize certain data without changing anything else, you can choose to check 'Add image to the front of the queue'.
Fetching tasks from the Queue
The project's users with the same role that you have set in your Queue settings will be able to see the Queue card and a button to 'Start your work'. On click, you will be redirected to an interface with an opportunity to fetch a batch of data or go to an annotation environment directly to perform individual tasks. This annotation environment has all the tools and usual components. However, the user is not able to choose to work on any image via the image gallery. They are limited to annotating the data assigned to an annotator via the Queue. On changing the status of the image, we recognize that the task is performed, and the image will be removed from the Queue to make place for a new task.
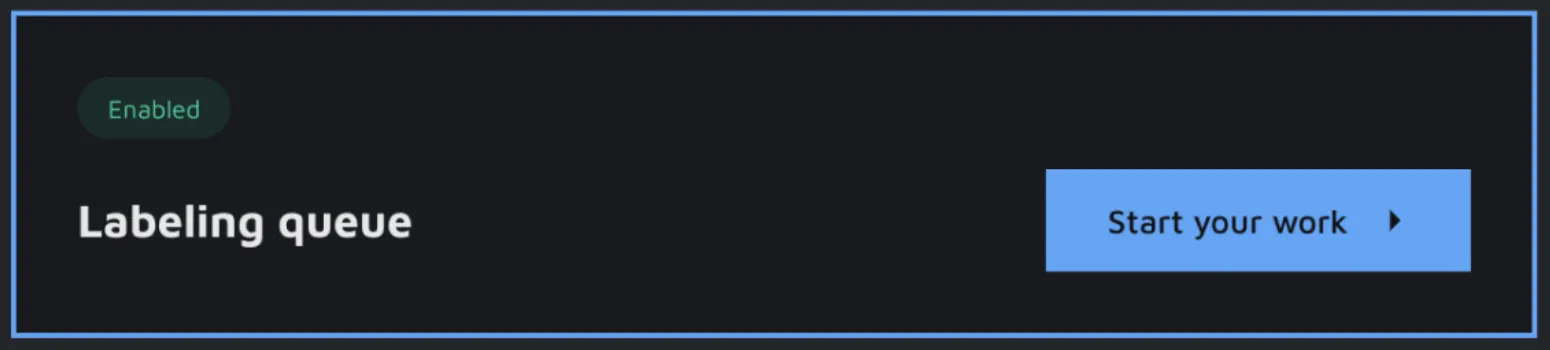
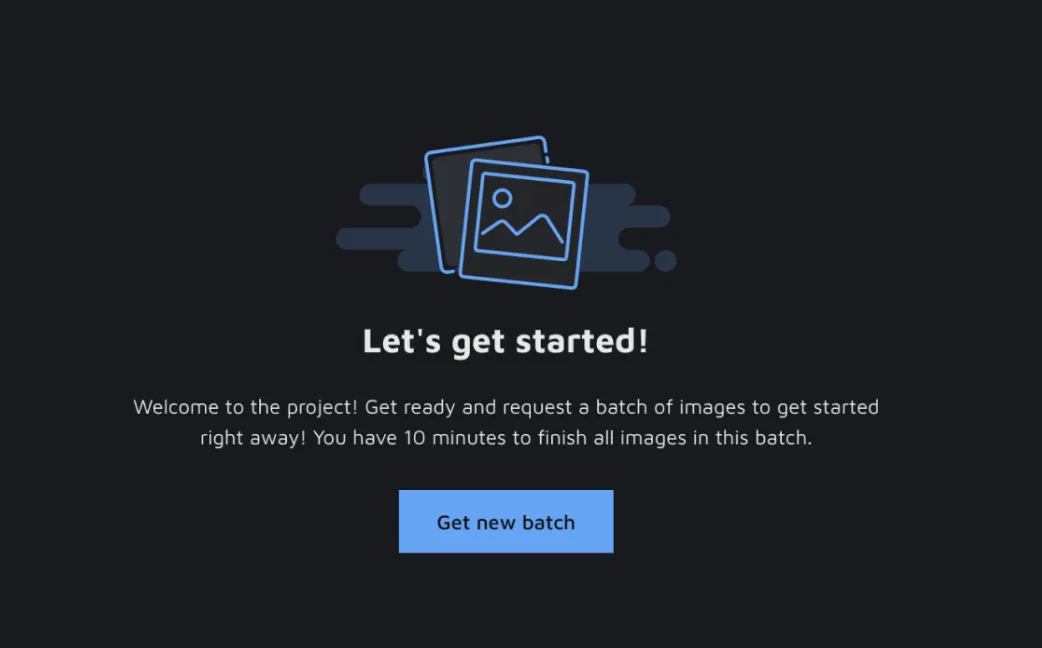
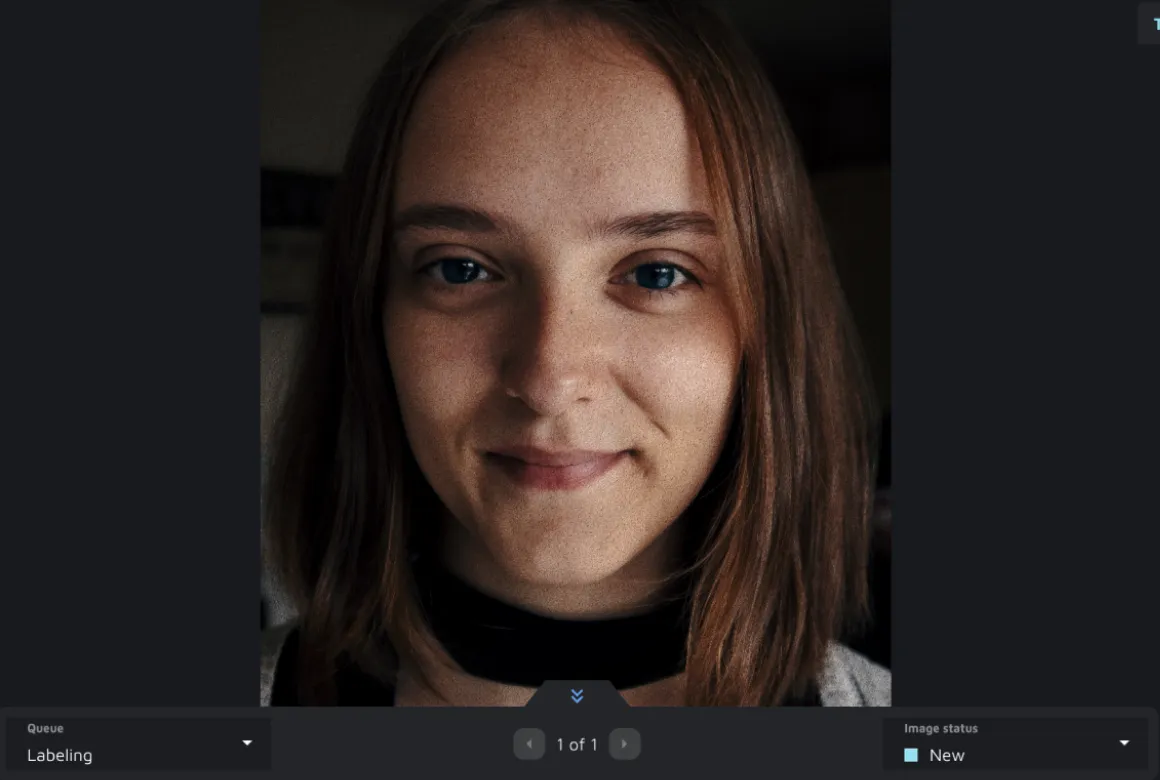
Whenever a task in the Labeling queue is done, you can choose to move it to the Review queue for a round of QA, check the annotations yourself, or add new data to the Labelling Queue. This opens up a lot of possibilities for the distribution of your data and the collaboration across the team.
