Blur
If you have ever worked on a Computer Vision project, you might know that using augmentations to diversify the dataset is the best practice. On this page, we will:
- Сover the Blur augmentation;
- Check out its parameters;
- See how Blur affects an image;
- And check out how to work with Blur using Python through the Albumentations library.
Let's jump in.
Blur augmentation explained
To define the term, Blur is a data augmentation technique that helps researchers to blur images with a certain likelihood.
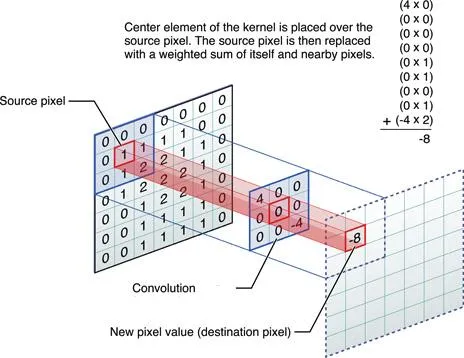
Blur filter is derived from convolution, a popular image-processing technique that changes the pixel's value with regard to the values of its surrounding pixels.
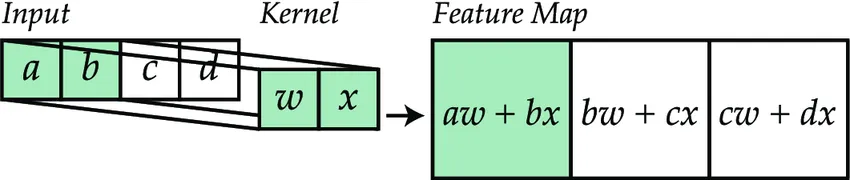
At the heart of convolution operation are Kernels, 1D or 2D grids of numbers that show how the neighboring pixels affect the given pixel's transformed value.
Source
Source
To count the value of a transformed pixel:
- Multiply each neighboring pixel's value with the corresponding Kernel value;
- Add the results;
- The resulting number is the transformed pixel's value;
- Repeat the process until the whole image is covered.
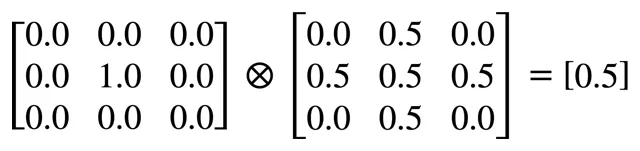
The simplest Kernel is the identity Kernel. It is named so since the only value it contains is 1, and applying it does not change the image.
As you can see below, to transform a given pixel, we multiply its value by 1 and all the surrounding pixel values by 0. The sum of the products will result in the initial pixel value (0.5 x 1 = 0.5).
Source
The output of the convolution can vary depending on the Kernel values.
For example, a matrix below is a Sharpen Kernel that sharpens the input image.

Source
To blur an image, we can use a 2D Kernel or box blur Kernel. It results in the average value of the neighboring pixels, decreasing the value of the transformed pixel.
In the example below, the sum of the Kernel values is 1, and each Kernel value is equal to 1/9:
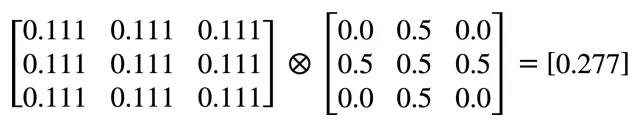
Source
- If the sum of the Kernel values is 1, the Kernel is normalized;
- If the sum is above 1, the output image is brighter than the input;
- If the sum is less than 1, the output image is darker than the input.
Besides the Kernel values, we can also change the size of the Kernel matrix itself:
- Increasing the Kernel size increases the influence of farther pixels on the given pixel's value.
- Decreasing the Kernel size, respectively, decreases the influence of farther pixels.
You can adjust the intensity of the Blur augmentation by setting the Blur limit parameters.
Blur augmentation parameters
- Blur limit - sets the range of Kernel used in the convolution process to blur the image. It can vary from 3 to 11. The larger the Kernel size, the more pronounced the blur effect is;
- Probability - sets the probability of the image being blurred. With a probability of 1, all images are blurred.
Blur augmentation visualized
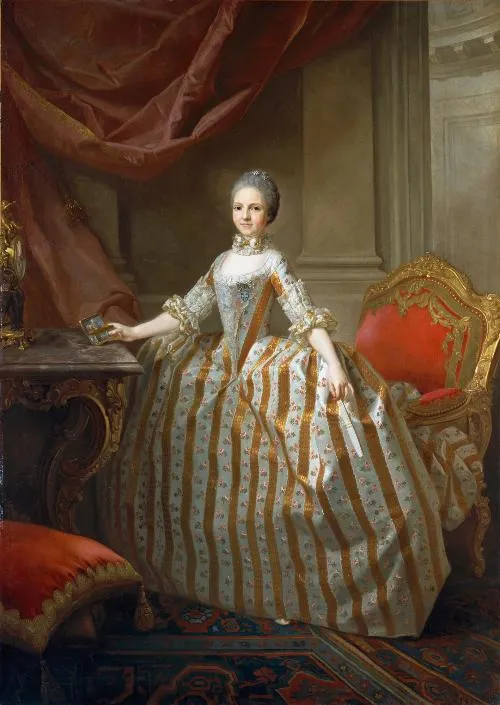

Source
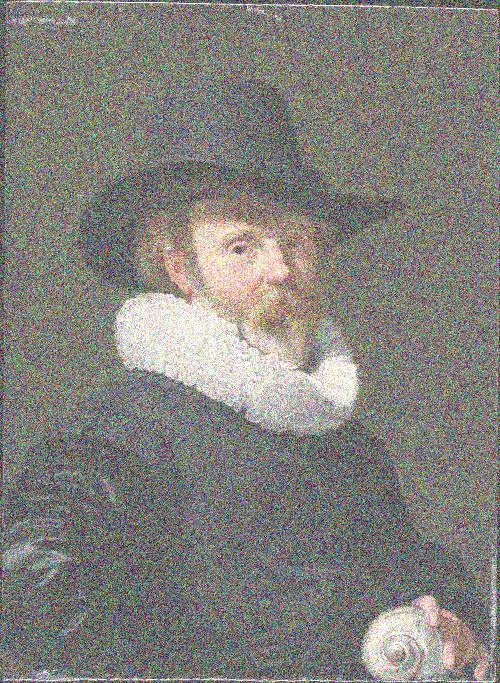

Source

Source
