Mask R-CNN
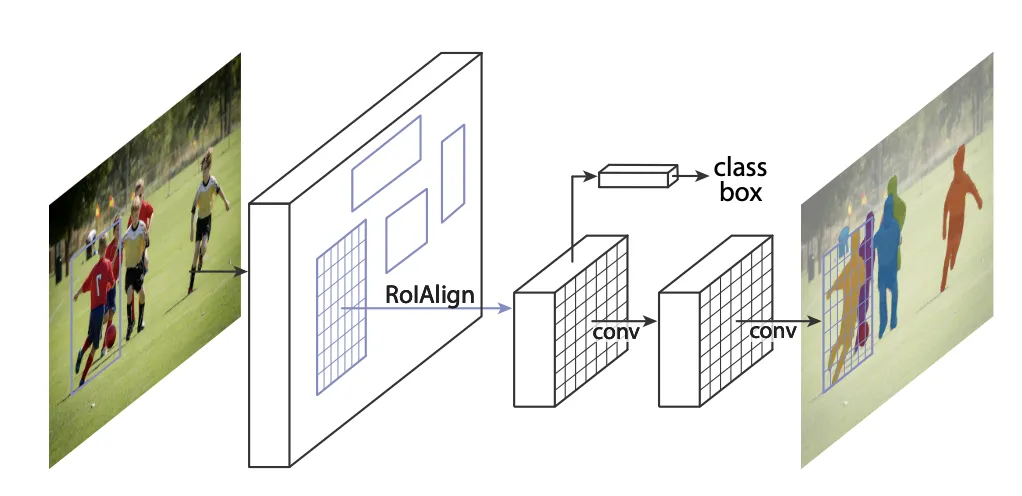
Mask R-CNN is the most used architecture for instance segmentation. It is almost built the same way as Faster R-CNN. The major difference is that there is an extra head that predicts masks inside the predicted bounding boxes.
Also, the authors replaced the RoI pool layer with the RoI align layer. RoI pool mappings are often a bit noisy. The difference is so small that it is negligible for object detection, but not when you want to create pixel-perfect masks for instance segmentation.
Hyperparameters
Typically, the following hyperparameters are tweaked when using Faster R-CNN:
Backbone network
Specifying the architecture for the network on which Faster R-CNN is built
Mostly, the backbone network is a ResNet variation.
IoU thresholds for RPN
These thresholds are used to decide if an anchor box generated contains an object or is part of the background.
Everything that is above the upper IoU threshold of the proposed anchor box and ground truth label will be classified as an object and forwarded. Everything below the lower threshold will be classified as background and the network will be penalized. For all the anchor boxes with an IoU between the thresholds, we're not sure if it's for- or background and we'll just ignore them.
Empirically, setting the lower bound to 0.3 and the upper to 0.7 leads to robust results.
Number of convolution filters in the ROI box head
How many convolution filters the final layer to make the classification contains. To a certain degree, increasing the number of filters will enable the network to learn more complex features, but the effect vanishes if you add too many filters and the network will perform worse (see the original ResNet paper to understand why you cannot endlessly chain convolution filters).
A good default value is 4 conv filters.
Number of fully connected layers in the ROI box head
How many fully connected layers (FC) the last part of the network contains. Increasing the number of FCs can increase performance for a computational cost, but you might overfit the sub-network if you add too many.
Often, 2 FCs are used as starting point.
NMS number of proposals
Pre NMS
The maximum of proposals that are taken into consideration by NMS. The proposals are sorted descending after confidence and only the ones with the highest confidence are chosen.
Post NMS
The maximum of proposals that will be forwarded to the ROI box head. Again, the proposals are sorted descending after confidence and only the ones with the highest confidence are chosen.
Config for training
Low numbers of NMS proposals in training will result in a lower recall, but higher precision. Vice versa.
The default for post NMS number of proposals in training is 1000, pre NMS 4000.
Config for testing
Here, the number of NMS proposals for the simple forward pass, e.g., inference, is defined. Less NMS proposals will increase inference speed, but higher numbers yield greater performance.
If you don't need super-fast inference, a good default is 1000 for post NMS number of proposals and 2000 for pre NMS.
Pooler Sampling Ratio
After extracting the Region of Interests from the feature map, they should be adjusted to a certain dimension before feeding them to the fully connected layer that will later do the actual object detection. For this, ROI Align is used which makes use of points that would be sampled from a defined grid, to resize the ROIs. The number of points that we use is defined by Pooler Sampling Ratio.
If Pooler Sampling ratio is set to 2, then 2 * 2 = 4 points are used for the interpolation.
Pooler resolution
It is the spatial size to pool proposals before feeding them to the mask predictor, in model playground default value is set as 14.
Depth of Resnet model
It is the depth variant of resnet to use as the backbone feature extractor, in Model Playground depth can be set as 18/50/101/152
Weights
It's the weights to use for model initialization, and in Model Playground R50-FPN COCO or R50-FPN LVIS weights are used.
Code implementation
In Model playground, after creating a split for Instance segmentation/Object detection tweak the Hyper-parameters of Mask R-CNN:
- Backbone network:The Backbone is the Conv Net architecture that is to be used in the first step of Mask R-CNN. Here it's ResNet50.
- IoU Thresholds:IoU thresholds for considering objects as background or foreground. Objects with IoU in between are ignored. The closer the predicted bounding box values are to the actual bounding box values the greater the intersection, and the greater the IoU value.
- Number of Fully Connected Layers:Number of hidden layers in the box predictor
NMS: In Object Detection, the objects in the image can be of different sizes and shapes, and to capture each of these perfectly, the algorithms that are used create multiple bounding boxes. (left image). Ideally, for each object in the image, we must have a single bounding box. To select the best bounding box, from the multiple predicted bounding boxes, these object detection algorithms use non-max suppression. This technique is used to “suppress” the less likely bounding boxes and keep only the best one. It takes into account the IoU Thresholds
- Post NMS parameters: This step is different for training and testing. In training, we select top N (default = 2000) proposals based on their corresponding objectness score from all proposals of all images in an entire batch. In testing, N proposals are selected for each image in the batch and kept separately.
- Pre NMS parameters: Selection of top k anchors based on their corresponding objectness score.
- The depth of the resnet model: The depth variant of resnet to use as the backbone feature extractor
- Weights: Weights to use for model initialization (R50-FPN COCO)
- Pooler Resolution: Size to pool proposals before feeding them to the box predictor. ROI Align/Pool gives a constant output of P X P irrespective of the proposal size, where P isPooler Resolution.
- Pooler Sampling Ratio: Number of bins for each sampling point
