Shear
If you have ever worked on a Computer Vision project, you might know that using augmentations to diversify the dataset is the best practice. On this page, we will:
Сover the Shear augmentation;
Check out its parameters;
See how Shear affects an image;
And check out how to work with Shear using Python through the Albumentations library.
Let’s jump in.
Shear augmentation explained
To define the term, Shear is a geometric augmentation that changes a form of an image along a specific axis to create a different perception angle.
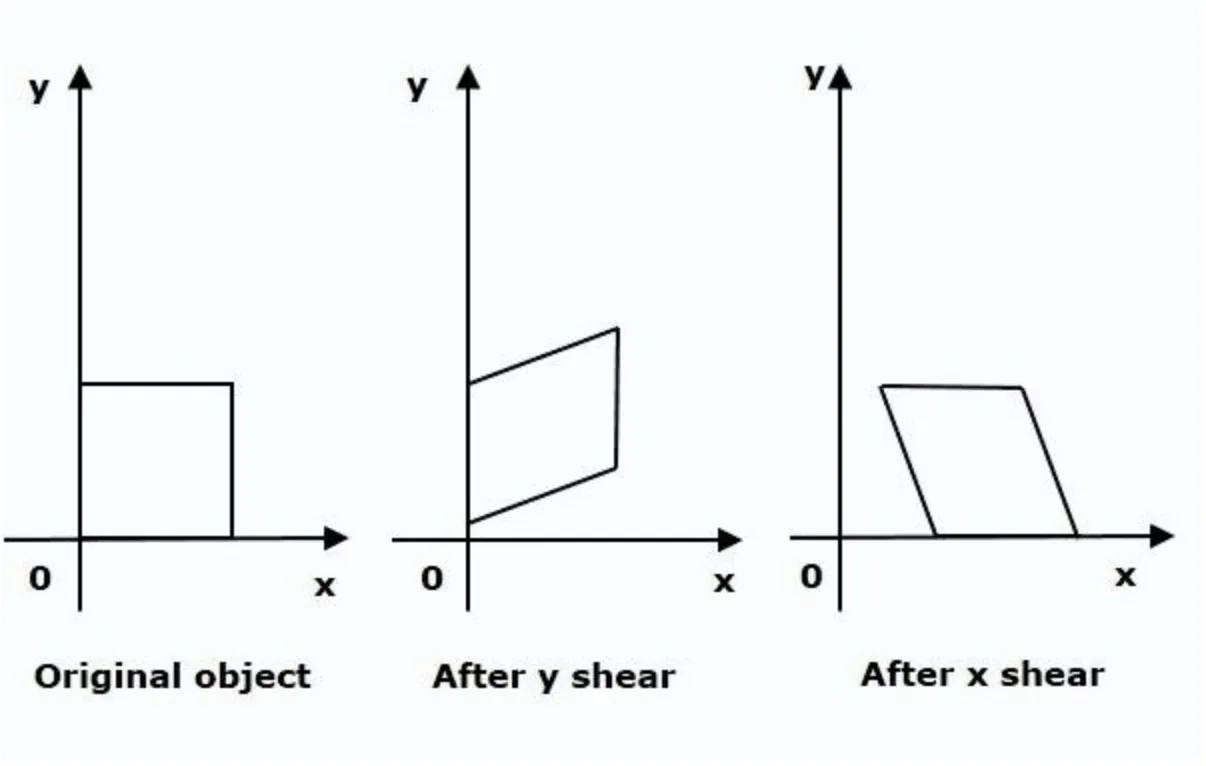
Source
As you can see in the picture above, Shear moves a side of an image, transforming its initial form of a square into a trapezoid. Shears are applied sequentially if you want to shear your image along the x- and y-axis. Data Scientists use Shear to augment pictures in such a way that an algorithm can identify an object from multiple angles.
Shear augmentation parameters
- Shear in degrees - specifies the range of degrees that is used to sample x- and y-shear angle values;
- Probability of applying transform - defines the likelihood of applying Shear to an image.
Shear augmentation visualized
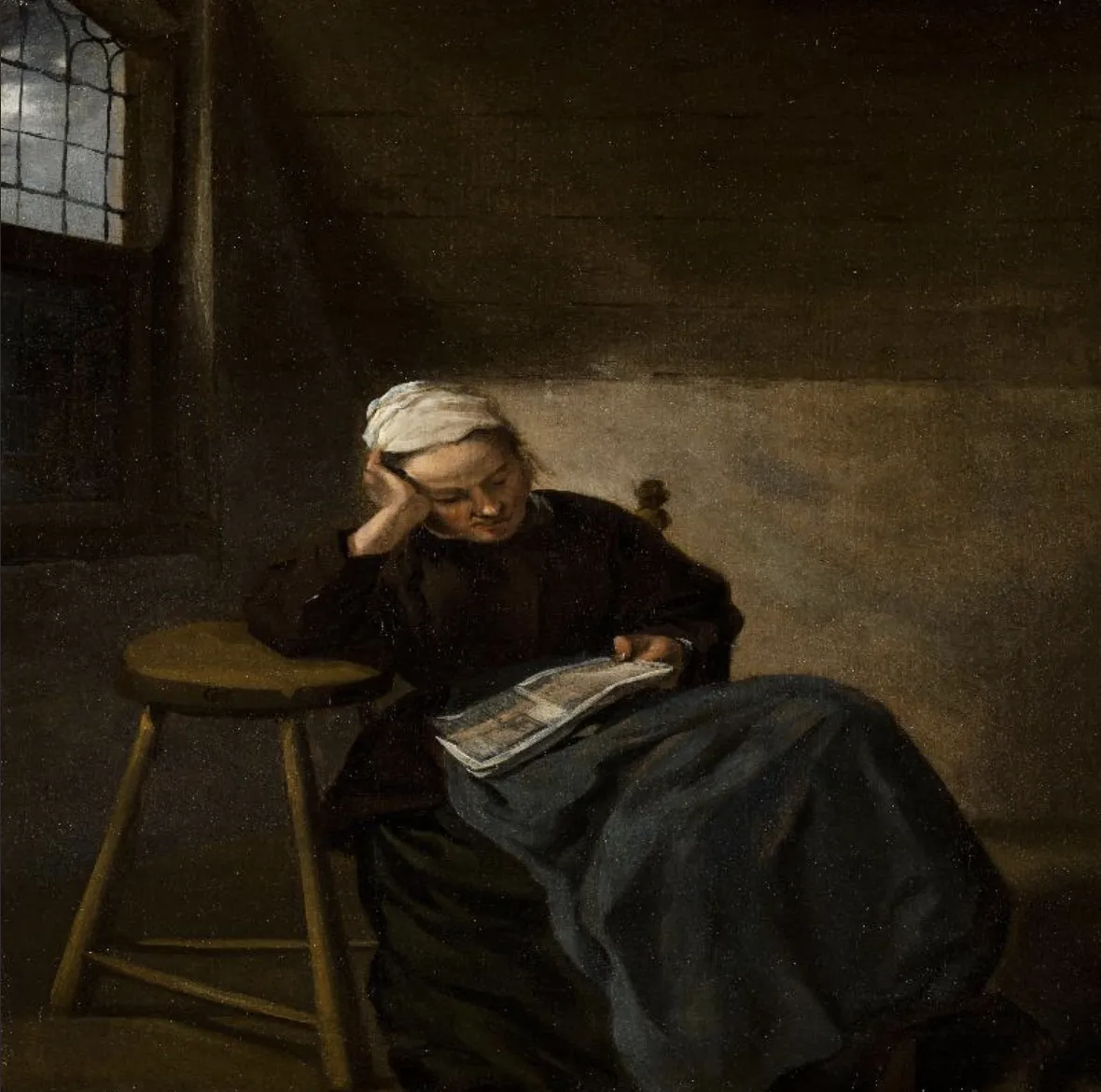

Source
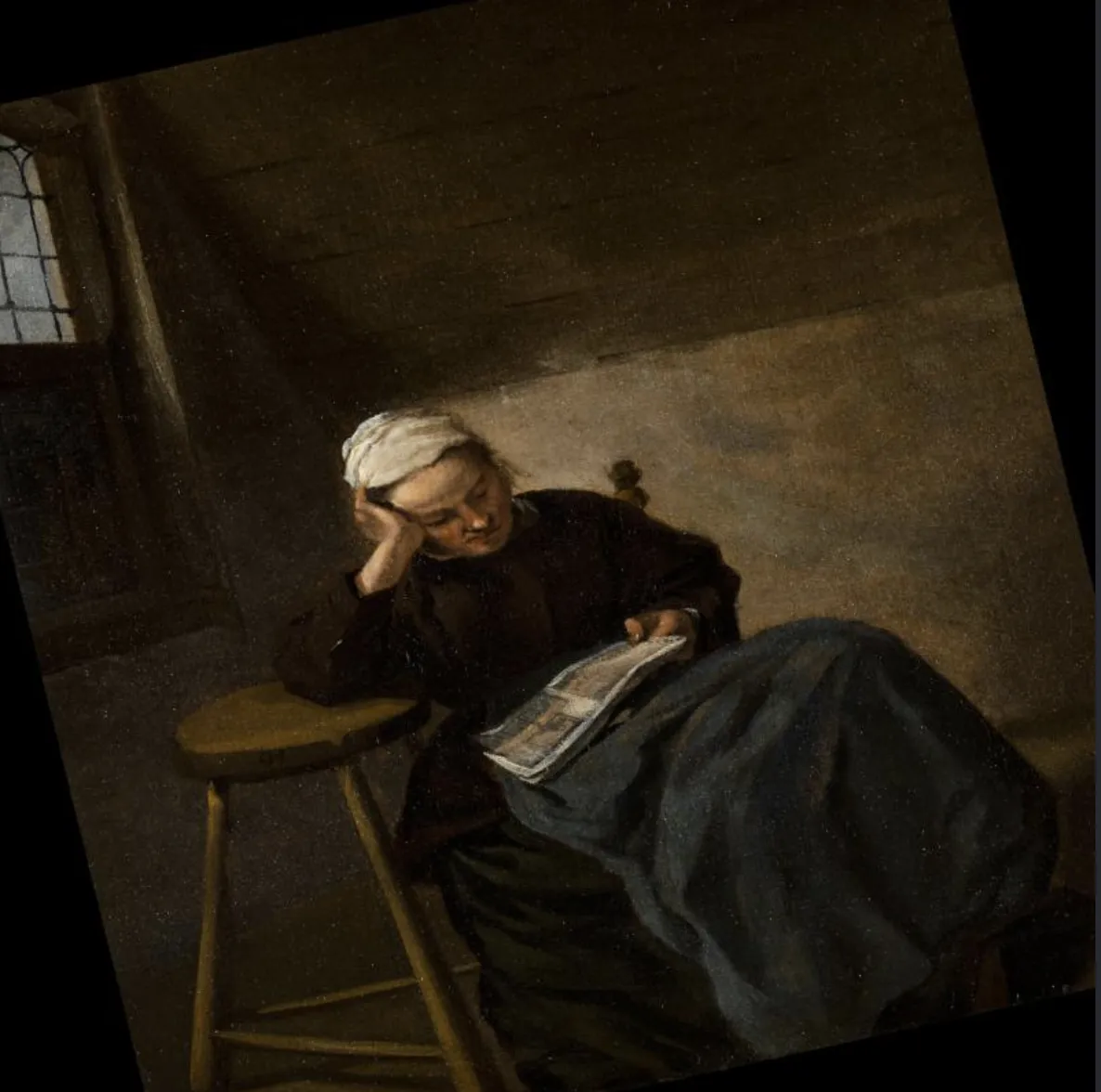

Source
